Electrical Testing Services
- Automated Printed Wiring Assembly Testing - Moving Probe-In Circuit Testing (Flying Prober)
- Automatic Electrical Testing - Electrical Testing Applications
- Capacitance - Electrical Testing Applications
- Conductance, Conductivity, Continuity - Electrical Testing Applications
- Contact Resistance - Electrical Testing Applications
- Data Acquisition - Electrical Testing Applications
- Dielectric Breakdown - Electrical Testing Applications
- Dielectric Strength - Electrical Testing Applications
- Dielectric Withstanding Voltage (DWV) - Electrical Testing Applications
- Dissipation Factor - Electrical Testing Applications
- Electrical Properties - Electrical Testing Applications
- HiPot - Electrical Testing Applications
- Inductance - Electrical Testing Applications
- Leakage - Electrical Testing Applications
- Power and Current Cycling - Electrical Testing Applications
- Q Factor - Electrical Testing Applications
- Resistance - Electrical Testing Applications
- Surface Insulation Resistance (SIR) - Electrical Testing Applications
- Volume and Surface Resistivity - Electrical Testing Applications
- Electrical Testing Related Standards
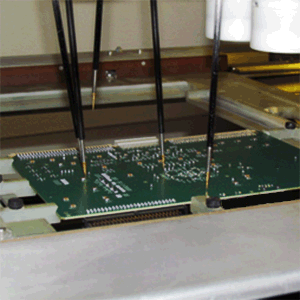
Moving Probe-In Circuit Testing (Flying Prober)
Traditional In-circuit test systems are used for the structural verification of printed wiring assemblies. The verification of component values, component orientations, detection of shorts and detection of opens with a guarded 2-wire or 4-wire measurement systems are the primary strengths of in-circuit test systems. In-circuit test systems rely on electrically connecting the printed wiring board to the test system with a custom fabricated bed-of-nails fixture which uses a large number of spring probes to make contact with every electrical net of the printed wiring board. Although bed-of-nails in-circuit programs execute quickly, the technique offers some significant limitations for some test scenarios. Bed-of-nails fixturing requires spring probe targets of a minimum size that may challenge the success of a printed wiring board layout and the spring probes generally cannot be placed closer than 1.27mm. Engineering changes which trigger a new the printed wiring board artwork can make an expensive bed-of-nails fixture obsolete and the fabrication time of a bed-of-nails fixture may also present challenges to the product release schedule as fixture fabrication can take weeks. The Flying Probe test systems, although slower in test execution, directly addresses most of the limitations of bed-of-nails testing solutions. The flying prober can reliably hit targets down to 150um. The most capable flying probe testers allow double sided moving probes with the ability to change the probe angle relative to the shape of the probing target and also possess the same measurement system as a bed-of-nails in-circuit tester. Flying probe testers are best used for prototype testing, testing of small volume products for which a bed-of-nails cost is not cost effective, testing of boards that have limited testability for probing targets or as a prescreen for technician troubleshooting of products that don't use in-line in-circuit testing in high first pass yield product assessment scenarios.
Applications:
- Prototype testing
- Small volume production
- Boards not conducive to bed-of-nails testing
- Troubleshooting pre-screen
Electrical Testing Applications
Accolade Engineering Solutions offers a variety of Electrical Testing Applications services. Contact us today to discuss your testing needs with someone who can provide you with the expert knowledge to determine the right testing solution for you.
Applications:
- Automatic Electrical Testing
- Capacitance
- Conductance, Conductivity, Continuity
- Contact Resistance
- Data Acquisition
- Dielectric Breakdown
- Dielectric Strength
- Dielectric Withstanding Voltage (DWV)
- Dissipation Factor
- Electrical Properties
- HiPot
- Inductance
- Leakage
- Power and Current Cycling
- Q Factor
- Resistance
- Temperature Coefficient
- Volume and Surface Resistivity
- And More...
Electrical Testing Related Standards
- ASTM B193 "Standard Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor Materials"
- ASTM B63 "Standard Test Method for Resistivity of Metallically Conducting Resistance and Contact Materials"
- ASTM D149 "Standard Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and Dielectric Strength of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials at Commercial Power Frequencies"
- ASTM D150 "Standard Test Method for AC Loss Characteristics and Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation"
- ASTM D1531 "Standard Test Methods for Relative Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) and Dissipation Factor by Fluid Displacement Procedures (Withdrawn 2012)"
- ASTM D229 "Standard Test Methods for Rigid Sheet and Plate Materials Used for Electrical Insulation"
- ASTM D2520 "Standard Test Methods for Complex Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials at Microwave Frequencies and Temperatures to 1650oC"
- ASTM D257 "Standard Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials"
- ASTM D4496 "Standard Test Method for D-C Resistance or Conductance of Moderately Conductive Materials"
- ASTM D877 "Standard Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids Using Disk Electrodes"
- ASTM D924 "Standard Test Method for Dissipation Factor (or Power Factor) and Relative Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Electrical Insulating Liquids"
- GMW3172 "General Specification for Electrical/Electronic Component Analytical/Development/Validation (A/D/V) Procedures for Conformance to Vehicle Environmental, Reliability, and Performance Requirements"
- EIA-364-06 "Contact Resistance Test Procedure for Electrical Connectors"
- EIA-364-20 "Withstanding Voltage Test Procedure for Electrical Connectors, Sockets and Coaxial Contacts"
- EIA-364-21 "Insulation Resistance Test Procedure for Electrical Connectors, Sockets and Coaxial Contacts"
- EIA-364-23 "Low Level Contact Resistance Test Procedure for Electrical Connectors and Sockets"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.10 "Insulation Resistance, Multilayer Printed Wiring (Between Layers)"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.11 "Insulation Resistance, Multilayer Printed Wiring (Within a Layer)"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.12 "Interconnection Resistance, Multilayer Printed Wiring"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.13 "Resistance of Copper Foil"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.14 "Resistivity of Copper Foil"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.17.1A "Volume and Surface Resistivity of Dielectric Materials"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.2 "Capacitance of Insulating Materials"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.5 "Dielectric Constant of Printed Wiring Materials"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.5.2 "Dielectric Constant and Dissipation Factor of Printed Wiring Board Material--Clip Method"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.5.4 "Dielectric Constant and Dissipation Factor of Printed Wiring Board Material--Micrometer Method"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.5.6 "Non-Destructive Full Sheet Resonance Test for Permittivity of Clad Laminates"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.6 "Dielectric Breakdown of Rigid Printed Wiring Material"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.6.1 "Solder Mask - Dielectric Strength"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.6.2 "Electric Strength of Printed Wiring Material"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.6.3 "Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and Dielectric Strength"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.5.7 "Dielectric Withstanding Voltage, PWB"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.6.14.1 "Electrochemical Migration Resistance Test"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.6.3.3 "Surface Insulation Resistance, Fluxes"
- IPC-TM-650, Method 2.6.3.7 "Surface Insulation Resistance"
- MIL-STD-202 Method 301 "Dielectric withstanding voltage"
- MIL-STD-202 Method 302 "Insulation resistance"
- MIL-STD-202 Method 303A "DC resistance"
- MIL-STD-202 Method 304 "Resistance temperature characteristic"
- MIL-STD-202 Method 305A "Capacitance"
- MIL-STD-202 Method 306 "Quality factor (Q)"
- MIL-STD-202 Method 307 "Contact resistance"
- MIL-STD-883 Method 1003 "Insulation resistance"
Copyright (c) 2014 accoladeeng.com. All rights reserved. | Design by FreeCSSTemplates.org.